Deep Residual Networks学习(二)
由ypyu创建,最终由bqirn5b7 被浏览 453 用户
 通过上次在Cifar10上复现ResNet的结果,我们得到了上表,最后一栏是论文中的结果,可以看到已经最好的初始化方法(MSRA)已经和论文中的结果非常接近了!今天我们完全按照论文中的实验环境,复现一下ResNet论文中的结果。
通过上次在Cifar10上复现ResNet的结果,我们得到了上表,最后一栏是论文中的结果,可以看到已经最好的初始化方法(MSRA)已经和论文中的结果非常接近了!今天我们完全按照论文中的实验环境,复现一下ResNet论文中的结果。
上次的论文复现主要和原文中有两点不同:
Data Augmentation
Cifar10中的图像都是32X32的,论文中对测试集中的每张图在每边都扩展了4个像素,得到40X40的图像,在训练时随机crop出32X32的图像进行训练,而对测试集不做任何操作
import lmdb
import cv2
import caffe
from caffe.proto import caffe_pb2
env1=lmdb.open('cifar10_train_lmdb')
txn1=env1.begin()
cursor=txn1.cursor()
datum=caffe_pb2.Datum()
env2=lmdb.open('cifar10_pad4_train_lmdb',map_size=50000*1000*10)
txn2=env2.begin(write=True)
count=0
for key,value in cursor:
datum.ParseFromString(value)
label=datum.label
data=caffe.io.datum_to_array(datum)
img=data.transpose(1,2,0)
pad=cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,4,4,4,4,cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)
array=pad.transpose(2,0,1)
datum1=caffe.io.array_to_datum(array,label)
str_id='{:08}'.format(count)
txn2.put(str_id,datum1.SerializeToString())
count+=1
if count%1000 ==0:
print('already handled with {} pictures'.format(count))
txn2.commit()
txn2=env2.begin(write=True)
txn2.commit()
env2.close()
env1.close()
程序很容易理解,最关键的是这句:
pad=cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,4,4,4,4,cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)
使用cv2的makeBorder函数扩展4个像素,运行后本地就会得到cifar10_pad4_train_lmdb了,注意,均值文件也需要重新生成,用于训练集数据
Different Shortcut Structure
 这是将网络结构借助ethereon绘制出来的部分截图,上面的红字代表这一层的卷积过滤器的数量,可以看到在filter数量加倍之后,shortcut结构没法直接相加了,所以原文中采用了PadChannel的结构,将多余的Channel全部补零,主要结构就是上图所示,先用一个average pooling层将feature map的size减半,再使用PadChannel增加16层的零filter层,我们将这种方法称为zero-padding法(亦即论文中的option A),这种方法的优点是接近于恒等层,不会引入新的参数。但是caffe目前不支持这种zero-padding的方法,所以我们需要向caffe中添加PadChannel层:
这是将网络结构借助ethereon绘制出来的部分截图,上面的红字代表这一层的卷积过滤器的数量,可以看到在filter数量加倍之后,shortcut结构没法直接相加了,所以原文中采用了PadChannel的结构,将多余的Channel全部补零,主要结构就是上图所示,先用一个average pooling层将feature map的size减半,再使用PadChannel增加16层的零filter层,我们将这种方法称为zero-padding法(亦即论文中的option A),这种方法的优点是接近于恒等层,不会引入新的参数。但是caffe目前不支持这种zero-padding的方法,所以我们需要向caffe中添加PadChannel层:
 看一下官方关于添加新层的说明,主要是以下四个文件:
看一下官方关于添加新层的说明,主要是以下四个文件:
1.pad_channel_layer.hpp添加到include/caffe/layers:
#ifndef CAFFE_PAD_CHANNEL_LAYER_HPP_
#define CAFFE_PAD_CHANNEL_LAYER_HPP_
#include "caffe/blob.hpp"
#include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/proto/caffe.pb.h"
namespace caffe {
/*
* @brief zero-padding channel to extend number of channels
*
* Note: Back-propagate just drop the pad derivatives
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class PadChannelLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
public:
explicit PadChannelLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual inline const char* type() const { return "PadChannel"; }
virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 1; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
protected:
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
int num_channels_to_pad_;
};
} // namespace caffe
#endif // CAFFE_PAD_CHANNEL_LAYER_HPP_
2.pad_channel_layer.cpp添加到src/caffe/layers
#include "caffe/layers/pad_channel_layer.hpp"
namespace caffe {
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
CHECK_NE(top[0], bottom[0]) << this->type() << " Layer does not "
"allow in-place computation.";
num_channels_to_pad_ = this->layer_param_.pad_channel_param().num_channels_to_pad();
CHECK_GT(num_channels_to_pad_, 0) << "num channels to pad must greater than 0!";
}
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
vector<int> top_shape = bottom[0]->shape();
top_shape[1] += num_channels_to_pad_;
top[0]->Reshape(top_shape);
}
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
int num = bottom[0]->num();
int channels = bottom[0]->channels();
int dim = bottom[0]->height() * bottom[0]->width();
int channel_by_dim = channels * dim;
for (int n = 0; n < num; n++){
caffe_copy(channel_by_dim, bottom_data, top_data);
bottom_data += channel_by_dim;
top_data += channel_by_dim;
caffe_set(num_channels_to_pad_ * dim, Dtype(0), top_data);
top_data += num_channels_to_pad_ * dim;
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
int num = bottom[0]->num();
int channels = bottom[0]->channels();
int dim = bottom[0]->height() * bottom[0]->width();
int channel_by_dim = channels * dim;
for (int n = 0; n < num; n++){ // just drop the padding derivatives part.
caffe_copy(channel_by_dim, top_diff, bottom_diff);
top_diff += (channels + num_channels_to_pad_) * dim;
bottom_diff += channel_by_dim;
}
}
INSTANTIATE_CLASS(PadChannelLayer);
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(PadChannel);
} // namespace caffe
3.pad_channel_layer.cu添加到src/caffe/layers:
#include "caffe/layers/pad_channel_layer.hpp"
namespace caffe {
// Copy (one line per thread) from one array to another, with arbitrary
// strides in the last two dimensions.
template <typename Dtype>
__global__ void pad_forward_kernel(const int dst_count, const int src_channels, const int dst_channels,
const int dim, const Dtype* src, Dtype* dst){
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, dst_count)
{
int num = index / (dim * dst_channels);
int dst_c = index / dim % dst_channels;
int pixel_pos = index % dim;
if (dst_c < src_channels)
dst[index] = src[num * src_channels * dim + dst_c * dim + pixel_pos];
else
dst[index] = Dtype(0);
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top){
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->gpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_gpu_data();
int src_channels = bottom[0]->channels();
int dim = bottom[0]->height() * bottom[0]->width();
int dst_channels = src_channels + num_channels_to_pad_;
const int dst_count = top[0]->count();
pad_forward_kernel<Dtype> << <CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(dst_count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS >> >(
dst_count, src_channels, dst_channels, dim, bottom_data, top_data);
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
}
template <typename Dtype>
__global__ void pad_backward_kernel(const int bottom_count, const int bottom_channels, const int top_channels,
const int dim, const Dtype* top, Dtype* bottom)
{
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, bottom_count)
{
int num = index / (dim * bottom_channels);
int bottom_c = index / dim % bottom_channels;
int pixel_pos = index % dim;
bottom[index] = top[num * top_channels * dim + bottom_c * dim + pixel_pos];
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void PadChannelLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff();
int bottom_count = bottom[0]->count();
int bottom_channels = bottom[0]->channels();
int dim = bottom[0]->height() * bottom[0]->width();
int top_channels = bottom_channels + num_channels_to_pad_;
pad_backward_kernel<Dtype> << <CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(bottom_count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS >> >(
bottom_count, bottom_channels, top_channels, dim, top_diff, bottom_diff);
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
}
INSTANTIATE_LAYER_GPU_FUNCS(PadChannelLayer);
} // namespace caffe
4.向caffe.proto中添加对应的message:
 好的,重新编译一次caffe之后,我们就可以使用PadChannel层了!
好的,重新编译一次caffe之后,我们就可以使用PadChannel层了!
下面我们看一下另外一种shortcut结构:
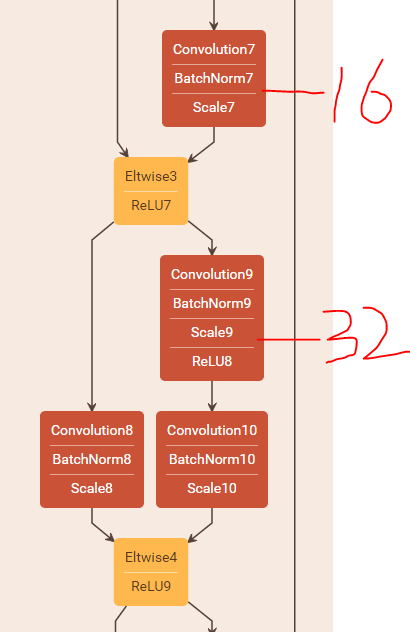 论文中将这种结构称为projection(亦即option B),使用1x1的卷积核来增加维度,这种方法会引入额外的参数!
论文中将这种结构称为projection(亦即option B),使用1x1的卷积核来增加维度,这种方法会引入额外的参数!
复现实验
好的,现在一切准备就绪,我们开始完整复现ResNet在Cifar10上的实验结果:
以下是一些参数设置:
weight_decay=0.0001 momentum=0.9batch_size=128learning_rate=0.1,0.01/32k,0.001/48kmax_iter=64k
当层数达到110层时,为加快收敛,我们先将learning_rate设置为0.01,迭代400次之后,再将learning_rate设置回0.1,正常进行训练
 A代表zero-padding,B代表projection,可以看出,Option A得到的结果和论文中基本一致,因为论文中采用的就是这种方法,而Option B却是所有结果中最好的,可以看出projection的方法是要优于zero_padding的方法的!
A代表zero-padding,B代表projection,可以看出,Option A得到的结果和论文中基本一致,因为论文中采用的就是这种方法,而Option B却是所有结果中最好的,可以看出projection的方法是要优于zero_padding的方法的!
接下来放几张训练的结果图:
首先是zero_padding:
 接下来是projection:
接下来是projection:

(这里暂时先忽略164的结果)
总结
至此,ResNet在cifar10的复现实验已经全部完成,我们完美复现了论文中的结果,甚至还得到了比论文中更好的结果!